Building a Large Japanese Web Corpus for Large Language Models
2404.17733

76
0
Abstract
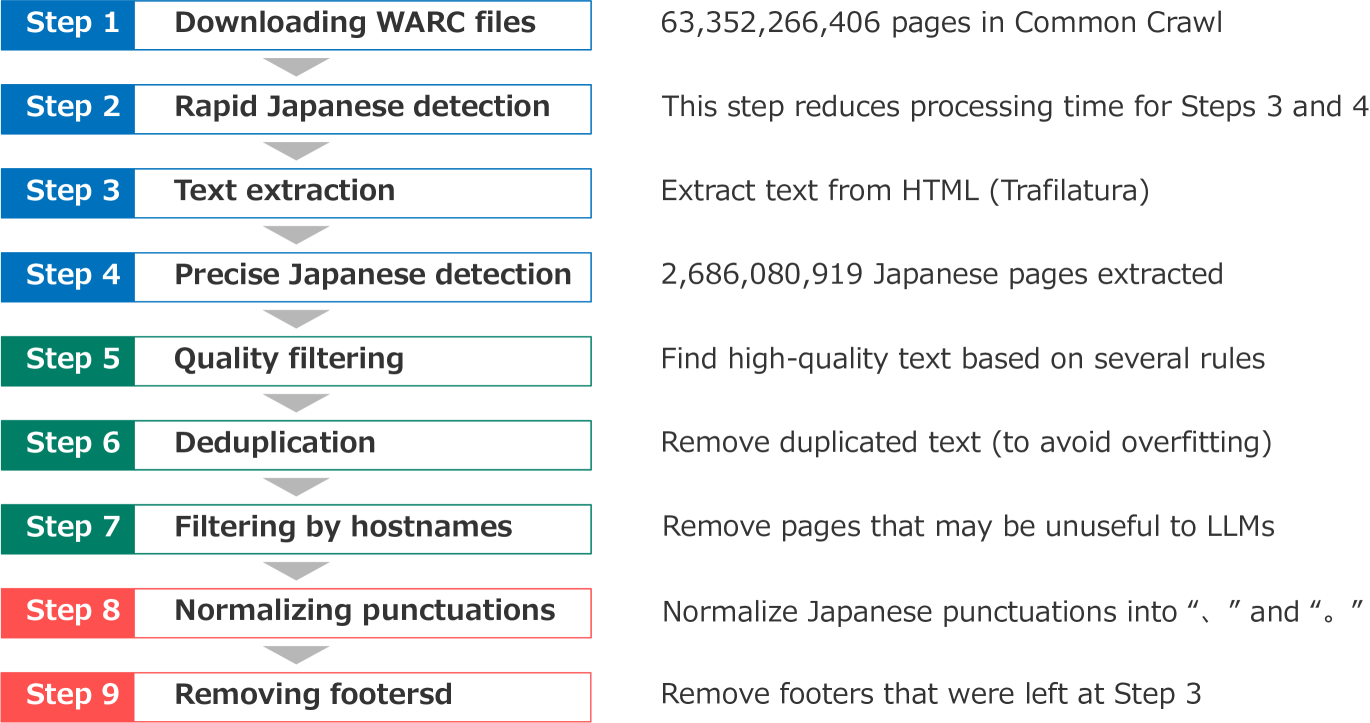
Open Japanese large language models (LLMs) have been trained on the Japanese portions of corpora such as CC-100, mC4, and OSCAR. However, these corpora were not created for the quality of Japanese texts. This study builds a large Japanese web corpus by extracting and refining text from the Common Crawl archive (21 snapshots of approximately 63.4 billion pages crawled between 2020 and 2023). This corpus consists of approximately 312.1 billion characters (approximately 173 million pages), which is the largest of all available training corpora for Japanese LLMs, surpassing CC-100 (approximately 25.8 billion characters), mC4 (approximately 239.7 billion characters) and OSCAR 23.10 (approximately 74 billion characters). To confirm the quality of the corpus, we performed continual pre-training on Llama 2 7B, 13B, 70B, Mistral 7B v0.1, and Mixtral 8x7B Instruct as base LLMs and gained consistent (6.6-8.1 points) improvements on Japanese benchmark datasets. We also demonstrate that the improvement on Llama 2 13B brought from the presented corpus was the largest among those from other existing corpora.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- This paper describes the construction of a large Japanese web corpus for use in training large language models.
- The authors collected a diverse set of web pages in Japanese from various sources, including news articles, blogs, and forums.
- They then processed the data to remove low-quality content and ensure the corpus is suitable for training large language models.
- The resulting corpus contains over 100 billion tokens, making it one of the largest publicly available Japanese language datasets.
Plain English Explanation
Building large language models, like the ones used for tasks such as natural language processing, requires a lot of text data to train on. In this paper, the researchers set out to create a large, high-quality corpus of Japanese web content that could be used to train these powerful AI models.
They gathered web pages from a variety of sources, including news sites, blogs, and online forums. This gave them a diverse set of text covering many different topics and styles of writing. However, not all web content is equally useful for training language models, so the researchers also spent time cleaning up the data, removing low-quality or irrelevant material.
After this processing, the final corpus contained over 100 billion words of Japanese text - an immense amount of data that can be used to pre-train large language models specifically for the Japanese language. This will enable the development of more capable and accurate AI systems that can understand and generate natural-sounding Japanese.
Technical Explanation
The authors first crawled a wide range of Japanese web pages from sources like news sites, blogs, and online forums. This gave them a diverse corpus covering many topics and writing styles. They then processed the raw web data to remove low-quality content, such as pages with excessive ads, broken links, or non-textual content.
To further improve the quality of the corpus, the researchers used a number of filtering techniques. This included removing near-duplicate pages, pages with low word counts, and pages with a high proportion of non-Japanese text. They also removed pages containing inappropriate or offensive content.
The final clean corpus contained over 100 billion tokens of Japanese text. This makes it one of the largest publicly available Japanese language datasets for training large language models. The authors believe this resource will enable the development of more capable Japanese language AI systems, including those for natural language processing and machine translation.
Critical Analysis
The researchers thoroughly describe their data collection and curation process, which is important for ensuring the quality and representativeness of the final corpus. However, they do not provide much detail on the specific sources of the web pages (e.g., the distribution across different types of sites) or the geographic/demographic coverage of the content.
Additionally, while the corpus size is impressive, the authors do not compare it to other available Japanese language datasets. It would be helpful to understand how this corpus fits in with the broader landscape of resources for Japanese NLP and language model training.
Lastly, the paper does not discuss potential biases or limitations of the web-crawled data, such as over-representation of certain topics or perspectives. Further analysis of the corpus characteristics and potential issues would strengthen the critical evaluation of this work.
Conclusion
This paper presents the construction of a large, high-quality Japanese web corpus containing over 100 billion tokens of text. The authors describe their thorough process of crawling, filtering, and cleaning the data to create a resource suitable for training advanced language models.
The resulting corpus is one of the largest publicly available Japanese language datasets, which will likely enable significant advancements in Japanese natural language processing and the development of more capable AI systems for the Japanese market. This work contributes an important building block for the future of Japanese language technology.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🎯
New!A Japanese-Chinese Parallel Corpus Using Crowdsourcing for Web Mining
Masaaki Nagata, Makoto Morishita, Katsuki Chousa, Norihito Yasuda

0
0
Using crowdsourcing, we collected more than 10,000 URL pairs (parallel top page pairs) of bilingual websites that contain parallel documents and created a Japanese-Chinese parallel corpus of 4.6M sentence pairs from these websites. We used a Japanese-Chinese bilingual dictionary of 160K word pairs for document and sentence alignment. We then used high-quality 1.2M Japanese-Chinese sentence pairs to train a parallel corpus filter based on statistical language models and word translation probabilities. We compared the translation accuracy of the model trained on these 4.6M sentence pairs with that of the model trained on Japanese-Chinese sentence pairs from CCMatrix (12.4M), a parallel corpus from global web mining. Although our corpus is only one-third the size of CCMatrix, we found that the accuracy of the two models was comparable and confirmed that it is feasible to use crowdsourcing for web mining of parallel data.
5/16/2024
Continual Pre-Training for Cross-Lingual LLM Adaptation: Enhancing Japanese Language Capabilities
Kazuki Fujii, Taishi Nakamura, Mengsay Loem, Hiroki Iida, Masanari Ohi, Kakeru Hattori, Hirai Shota, Sakae Mizuki, Rio Yokota, Naoaki Okazaki

0
0
Cross-lingual continual pre-training of large language models (LLMs) initially trained on English corpus allows us to leverage the vast amount of English language resources and reduce the pre-training cost. In this study, we constructed Swallow, an LLM with enhanced Japanese capability, by extending the vocabulary of Llama 2 to include Japanese characters and conducting continual pre-training on a large Japanese web corpus. Experimental results confirmed that the performance on Japanese tasks drastically improved through continual pre-training, and the performance monotonically increased with the amount of training data up to 100B tokens. Consequently, Swallow achieved superior performance compared to other LLMs that were trained from scratch in English and Japanese. An analysis of the effects of continual pre-training revealed that it was particularly effective for Japanese question answering tasks. Furthermore, to elucidate effective methodologies for cross-lingual continual pre-training from English to Japanese, we investigated the impact of vocabulary expansion and the effectiveness of incorporating parallel corpora. The results showed that the efficiency gained through vocabulary expansion had no negative impact on performance, except for the summarization task, and that the combined use of parallel corpora enhanced translation ability.
4/30/2024

101 Billion Arabic Words Dataset
Manel Aloui, Hasna Chouikhi, Ghaith Chaabane, Haithem Kchaou, Chehir Dhaouadi

0
0
In recent years, Large Language Models have revolutionized the field of natural language processing, showcasing an impressive rise predominantly in English-centric domains. These advancements have set a global benchmark, inspiring significant efforts toward developing Arabic LLMs capable of understanding and generating the Arabic language with remarkable accuracy. Despite these advancements, a critical challenge persists: the potential bias in Arabic LLMs, primarily attributed to their reliance on datasets comprising English data that has been translated into Arabic. This reliance not only compromises the authenticity of the generated content but also reflects a broader issue -the scarcity of original quality Arabic linguistic data. This study aims to address the data scarcity in the Arab world and to encourage the development of Arabic Language Models that are true to both the linguistic and nuances of the region. We undertook a large-scale data mining project, extracting a substantial volume of text from the Common Crawl WET files, specifically targeting Arabic content. The extracted data underwent a rigorous cleaning and deduplication process, using innovative techniques to ensure the integrity and uniqueness of the dataset. The result is the 101 Billion Arabic Words Dataset, the largest Arabic dataset available to date, which can significantly contribute to the development of authentic Arabic LLMs. This study not only highlights the potential for creating linguistically and culturally accurate Arabic LLMs but also sets a precedent for future research in enhancing the authenticity of Arabic language models.
5/6/2024
💬
Pretraining and Updating Language- and Domain-specific Large Language Model: A Case Study in Japanese Business Domain
Kosuke Takahashi, Takahiro Omi, Kosuke Arima, Tatsuya Ishigaki

0
0
Several previous studies have considered language- and domain-specific large language models (LLMs) as separate topics. This study explores the combination of a non-English language and a high-demand industry domain, focusing on a Japanese business-specific LLM. This type of a model requires expertise in the business domain, strong language skills, and regular updates of its knowledge. We trained a 13-billion-parameter LLM from scratch using a new dataset of business texts and patents, and continually pretrained it with the latest business documents. Further we propose a new benchmark for Japanese business domain question answering (QA) and evaluate our models on it. The results show that our pretrained model improves QA accuracy without losing general knowledge, and that continual pretraining enhances adaptation to new information. Our pretrained model and business domain benchmark are publicly available.
4/17/2024